Sequences and Flows
Sequence Term
In YAMLCord, the term sequence refers to conditional structures or functions.
YAMLCord is executed in sequences, which are executed one after the other, having to wait for the previous sequence to finish before starting the next one.
Indicating Sequences
All sequences are indicated within the top-level sequences field.
Sequences can be linear or forked.
Linear Sequences
In linear sequences, sequences are executed one after the other without interruptions or bifurcations that alter the flow.
Linear sequences are the simplest, having the best flow predictability and being the most common way of executing flows.
Example and Representation of Linear Sequences
sequences:
- create_message(): "😃 Hello @User! How is your day going on?"
- add_reaction(): "👋"
From the beginning to the end, the flow is linear, so all sequences will be executed one after the other, without interruptions or bifurcations.
Forked Sequences
In forked sequences, the flow can be altered by taking different flows depending on the result of a conditional.
Forked sequences are the most complex, having less flow predictability and being the most dynamic way to execute flows.
Example and Representation of Forked Sequences
sequences:
- if: "[user_id] eq [owner_id]"
then:
- create_message(): "✅ You are the owner of the server!"
else:
- create_message(): "❌ You are not the owner of the server!"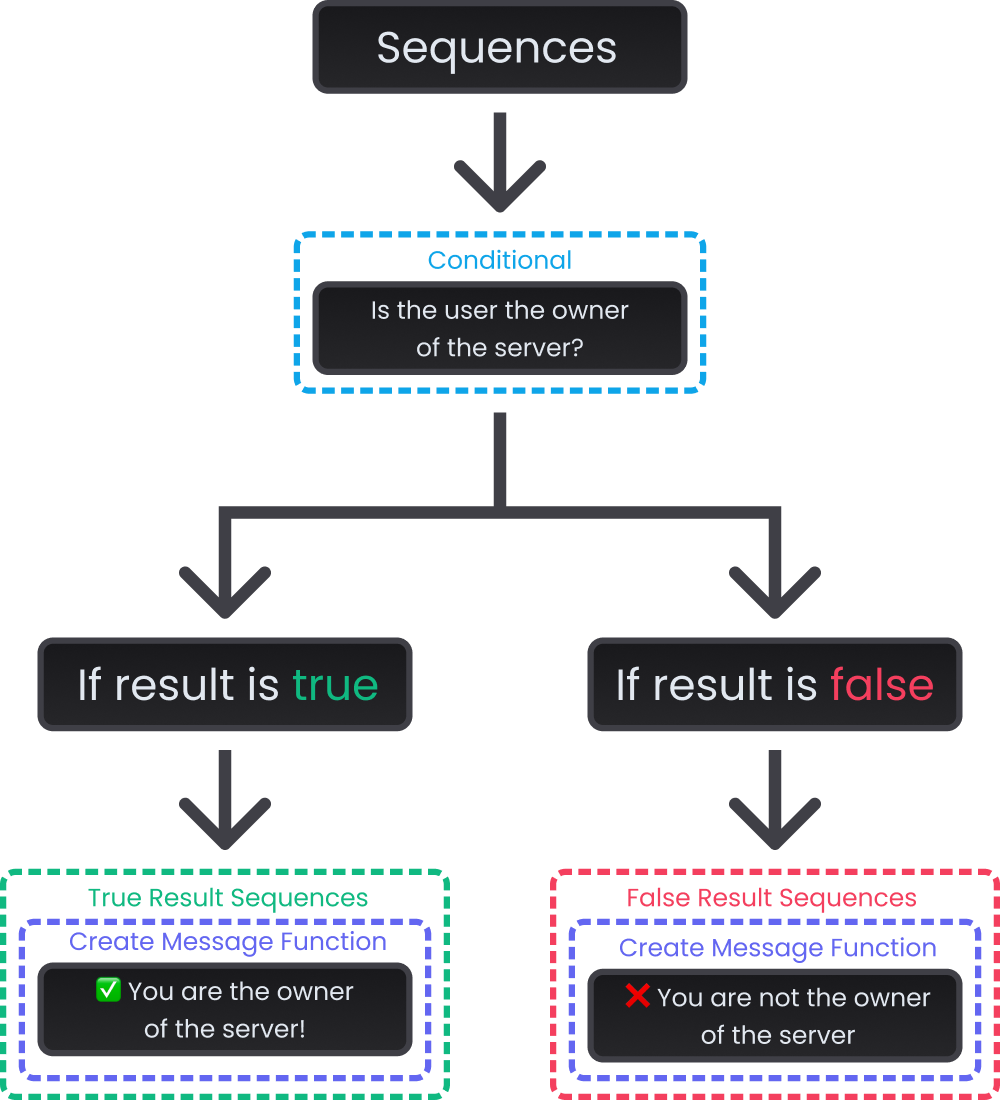
From the beginning to the conditional, the flow is linear, so all sequences will be executed one after the other, without interruptions or bifurcations.
When it reaches the conditional, the flow changes to a forked flow, and depending on the result of the conditional, one flow or the other will be executed, but never both flows will be executed.
- If the result is
true, only the sequences withinTrue Result Sequenceswill be executed. - If the result is
false, only sequences withinFalse Result Sequenceswill be executed.